500000
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The landscape mapping conducted by the NIBIO is based on a method developed by the US Forestry Service, adapted to Norwegian conditions. A landscape feature in the landscape reference system is a continuous area (polygon) with the same attributes assigned according to the classification criteria defined in the naitonal landscape reference system. The three-dimensional classification of the landscape is based more on a multidisciplinary understanding and holistic evaluation, than on traditional science and cartography. Studying six main components of the landscape is important in three-dimensional landscape mapping, while the relative importance of individual components varies between the different landscape regions. The main components are: major landforms; geological composition; water and waterways; vegetation; agricultural land and buildings. The reference system consists of a national map dividing the country in 45 landscape regions and 444 sub regions. Furthermore, 10 agricultural regions have been classified, emphasizing common preconditions for agriculture.
-

Vegetation polygons grouped into 16 classes of habitats. Vegetation maps provide a simplified image of the mosaic of vegetation types which constitute the natural plant cover. A vegetation type is a characteristic collection of plant species which will be found on places with similar growth conditions. A vegetation feature in the vegetation map is a continuous area (polygon) with the same attributes assigned according to the classification criteria of vegetation. In addition, each vegetation feature is classified according to main vetetation types (10 classes), habitats (16 classes) and suitability for sheep and cattle grazing. Today there are two mapping systems in Norway: one for detailed mapping at 1: 5000–20.000 and one for more general mapping at 1:20.000–50.000. The data on vegetation types from the detailed system can be combined with data relating to vegetation types in the general system.
-

Vegetation polygons classified according to suitability for cattle grazing (Very good; Good; Less good). Vegetation maps provide a simplified image of the mosaic of vegetation types which constitute the natural plant cover. A vegetation type is a characteristic collection of plant species which will be found on places with similar growth conditions. A vegetation feature in the vegetation map is a continuous area (polygon) with the same attributes assigned according to the classification criteria of vegetation. In addition, each vegetation feature is classified according to main vetetation types (10 classes), habitats (16 classes) and suitability for sheep and cattle grazing. Today there are two mapping systems in Norway: one for detailed mapping at 1: 5000–20.000 and one for more general mapping at 1:20.000–50.000. The data on vegetation types from the detailed system can be combined with data relating to vegetation types in the general system.
-

N500 Map Data is a generalisation of N250 Map Data and cartographically adapted to a scale of 1:300,000 - 1:700,000. N500 Map Data covers mainland Norway delimited by the national borders with neighbouring countries and the territorial boundaries in the sea.
-

Video observations to classify general biotopes. The map shows video observations that have been used to classify general biotopes in the areas investigated with video by MAREANO up to and including 2019 based on detailed video analyses. 45 biotopes are shown in different colours.
-

Vegetation polygons grouped into 45 classes of vegetation groups. Vegetation maps provide a simplified image of the mosaic of vegetation types which constitute the natural plant cover. A vegetation type is a characteristic collection of plant species which will be found on places with similar growth conditions. A vegetation feature in the vegetation map is a continuous area (polygon) with the same attributes assigned according to the classification criteria of vegetation. In addition, each vegetation feature is classified according to main vetetation types (10 classes), habitats (16 classes) and suitability for sheep and cattle grazing. Today there are two mapping systems in Norway: one for detailed mapping at 1: 5000–20.000 and one for more general mapping at 1:20.000–50.000. The data on vegetation types from the detailed system can be combined with data relating to vegetation types in the general system.
-

This data set contains the distribution of seabed sediments classified after genesis in mapped areas on the Norwegian shelf. The superficial deposit surface type describes the superficial deposits genesis. The data is based on the contents of the Quaternary map which are analogous (scale 1: 250,000 to 1: 500,000), or based on digital data from modern surveying.
-
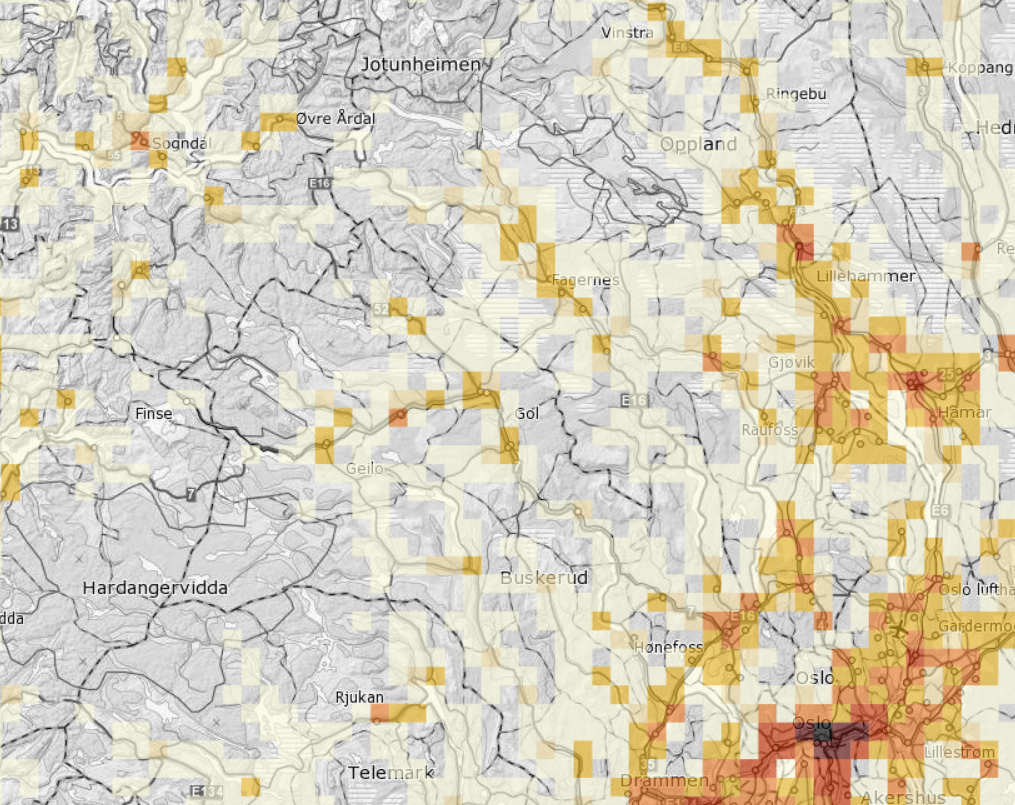
Dwelling statistics on grid 5000m x 5000m.
-

Bathyal seapen communities distribution model. In patches, the deep-sea seapen Umbellula encrinus is found in relatively high densities from half way down the continental slope (approximately 800 metres below sea level) and deeper. This large seapen can reach a height of more than two metres. There are often high densities of tube-building amphipods (Neohela) in areas with Umbellula.
-

N500 Map Data is a generalisation of N250 Map Data and cartographically adapted to a scale of 1:300,000 - 1:700,000. N500 Map Data covers mainland Norway delimited by the national borders with neighbouring countries and the territorial boundaries in the sea.
 geonetworktest
geonetworktest